Types of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis refers to the inflammation of the tonsils, two small masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the throat.
The primary causes of tonsillitis are viral and bacterial infections. To differentiate between the two, two key aspects must be evaluated: the characteristics of the inflammation and the presence or absence of associated symptoms.
Episodes of tonsillitis are often accompanied by pharyngeal inflammation, and vice versa. When both the tonsils and the pharynx are inflamed, the condition is referred to as pharyngotonsillitis.
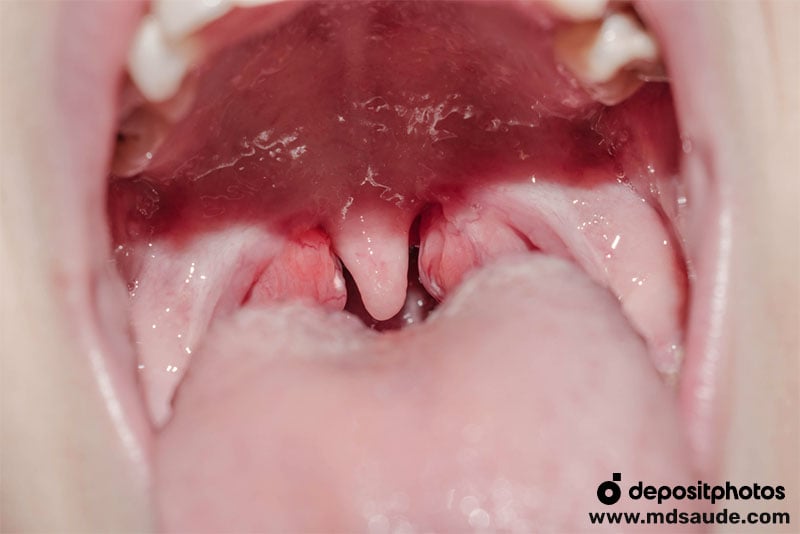
Images of Viral Tonsillitis or Pharyngitis
Viral tonsillitis/pharyngitis is caused by viruses such as Influenza virus, Adenovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), SARS-CoV-2, Coxsackievirus, among others.
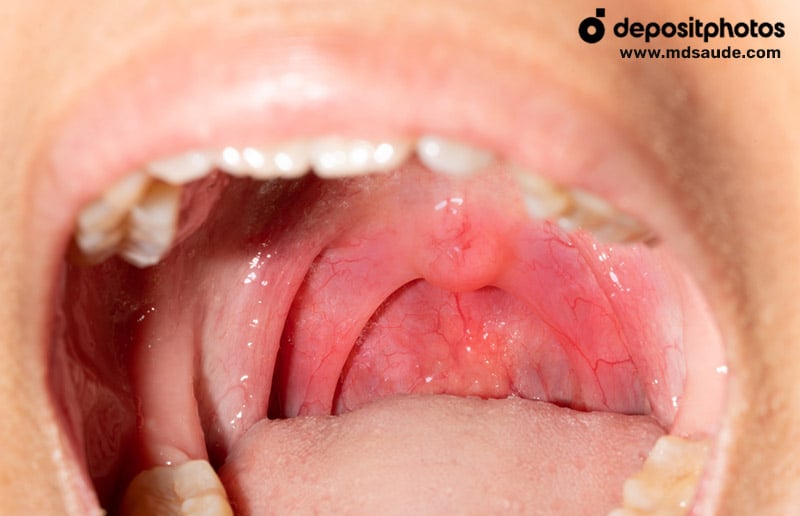
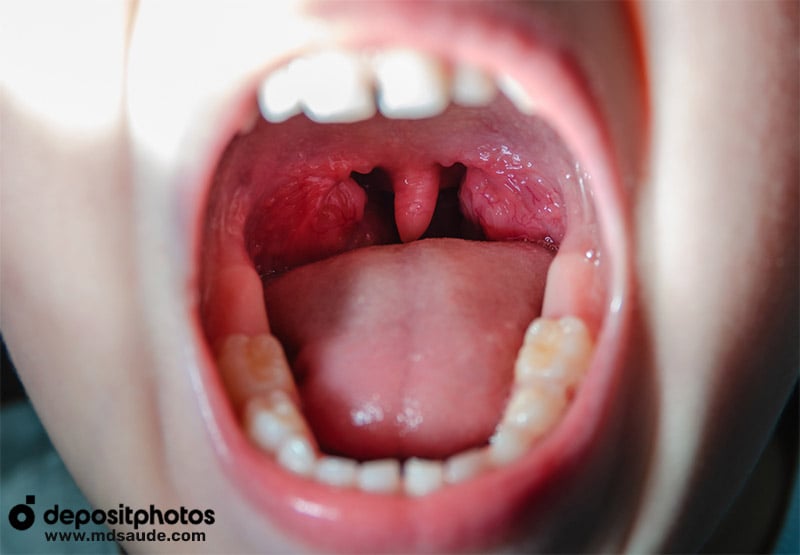
Common Symptoms of Viral Pharyngotonsillitis:
- Sore throat: usually the first symptom, often severe.
- Fever: when present, typically mild to moderate.
- Tonsillar swelling: redness, prominent blood vessels, and inflammation without pus.
- Ulcers in the pharynx: some viral infections cause small, painful ulcers in the throat.
- Pain while swallowing: common, ranging from moderate to severe.
- Hoarseness or voice changes: frequent when associated with viral laryngitis.
- Cold or flu-like symptoms: commonly accompanied by runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, cough, and general malaise.
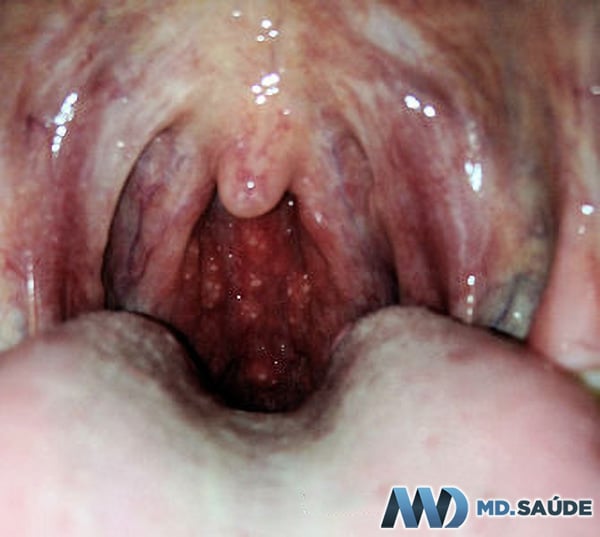
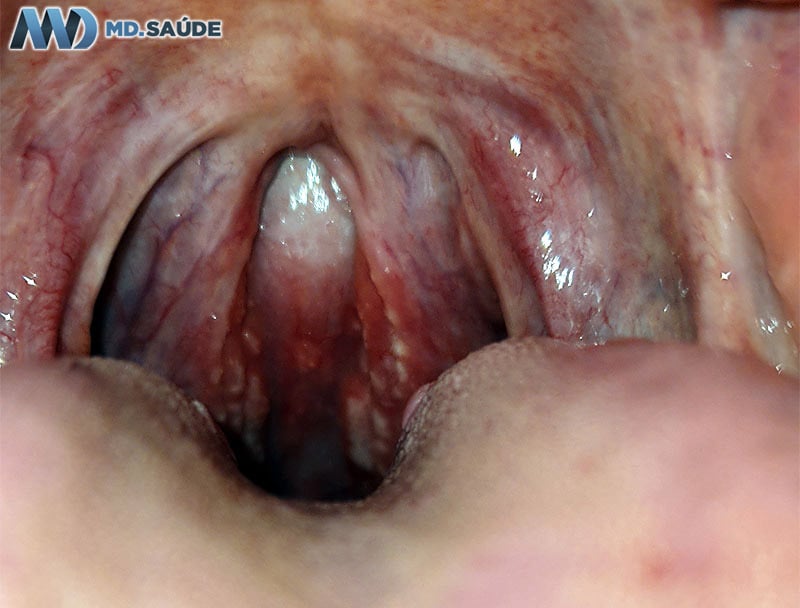
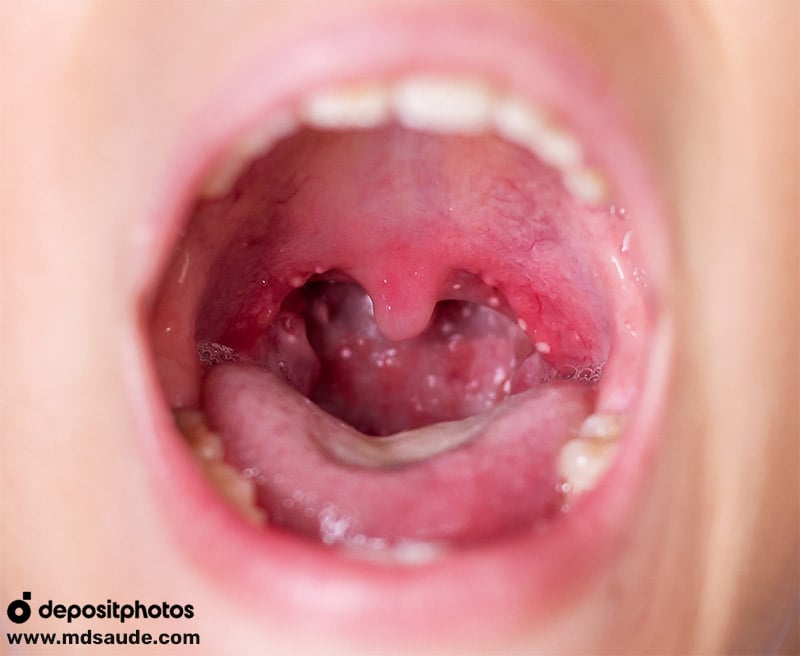
Some patients with mononucleosis can develop purulent tonsillitis, often with an appearance that looks like a mantle of pus covering the tonsils. In such cases, it can be difficult to distinguish between bacterial tonsillitis and mononucleosis without additional diagnostic tests.
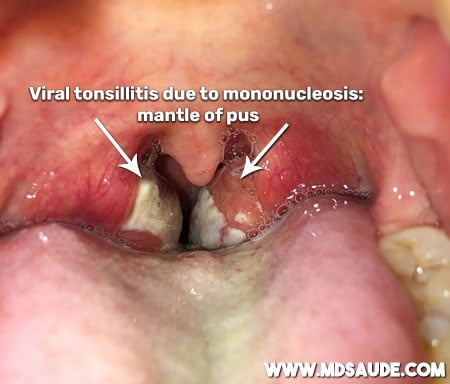
Images of Bacterial Tonsillitis or Pharyngitis
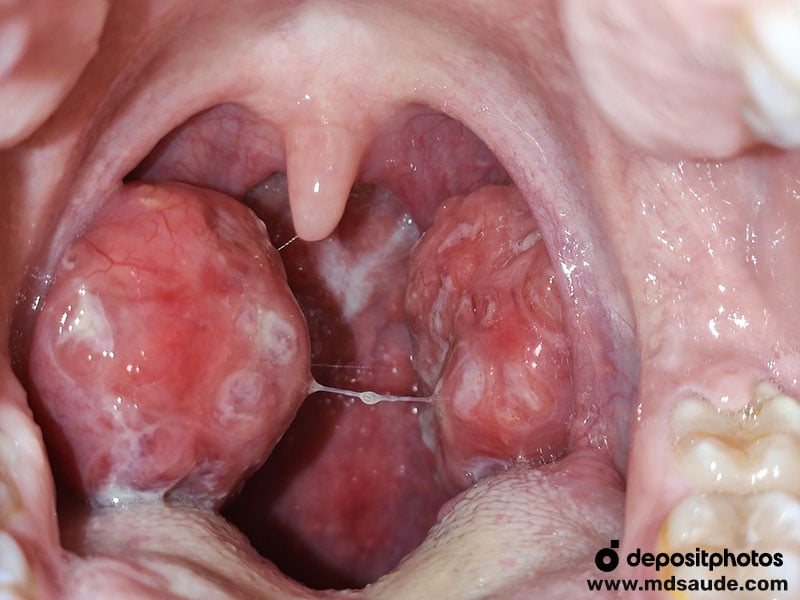
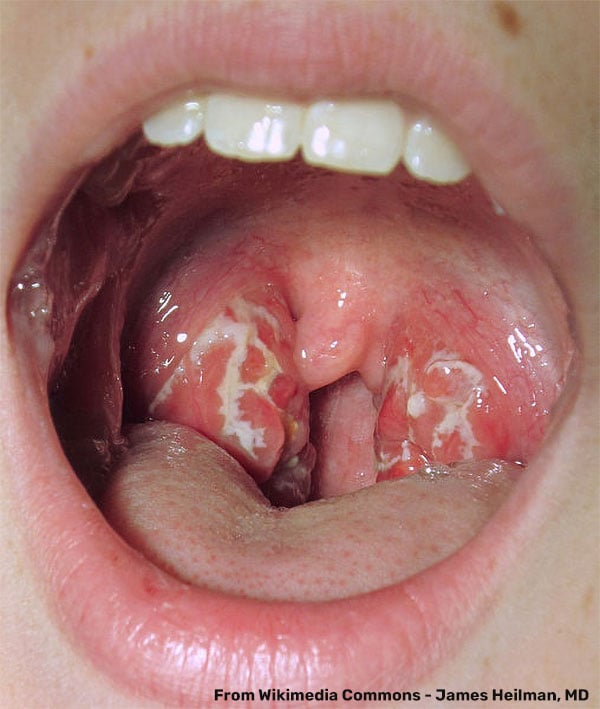
The most common form of bacterial tonsillitis is caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes, commonly known as group A streptococcus. The most characteristic sign of bacterial tonsillitis is the presence of pus on the tonsils.
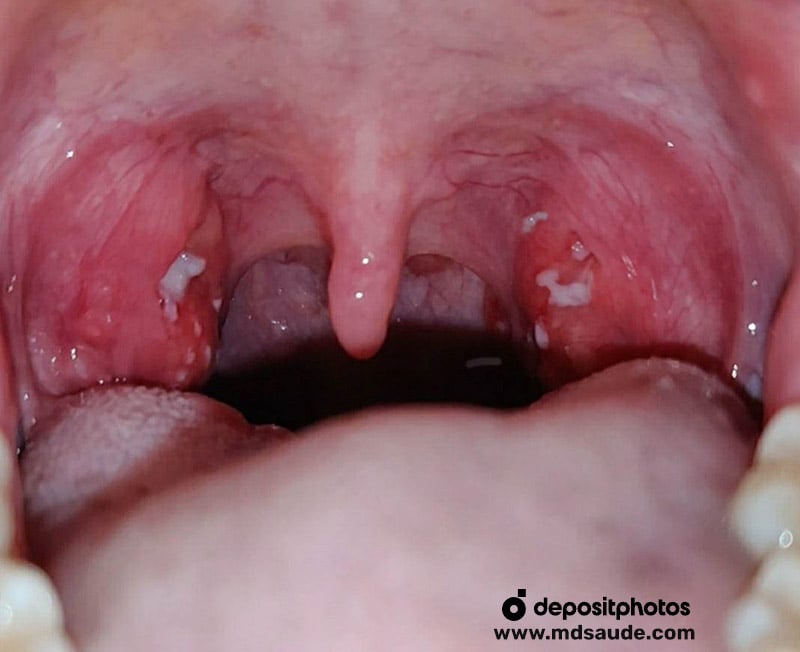
Bacterial tonsillitis, particularly those caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, tend to have distinct characteristics:
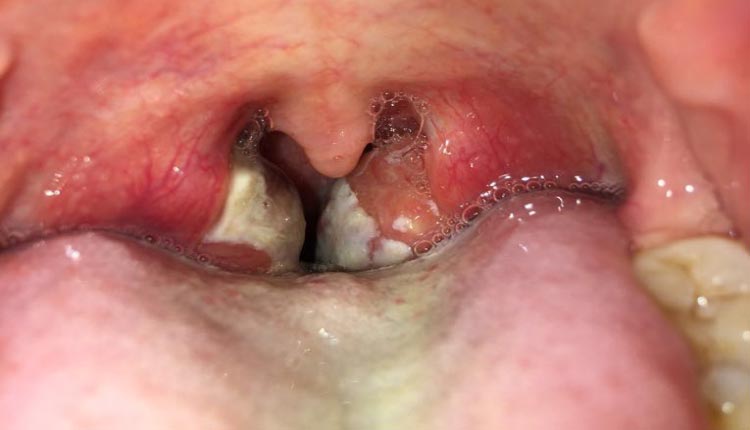
- Purulent exudate: tonsils often present white or yellow patches of pus, a finding rarely seen in viral infections.
- Intense redness with well-defined margins: the inflammation is usually severe, with bright, sharply demarcated redness.
- Significant tonsillar swelling: the tonsils may become substantially enlarged and often tender to touch.
- Severe sore throat: pain while swallowing is generally more intense in bacterial than in viral infections.
- Foul breath (halitosis): more pronounced in bacterial infections due to bacterial overgrowth and tissue breakdown.
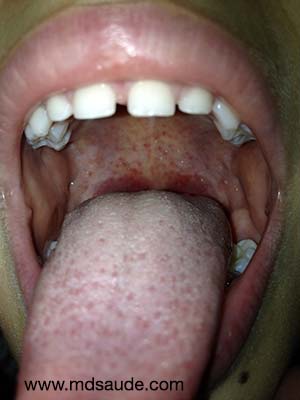
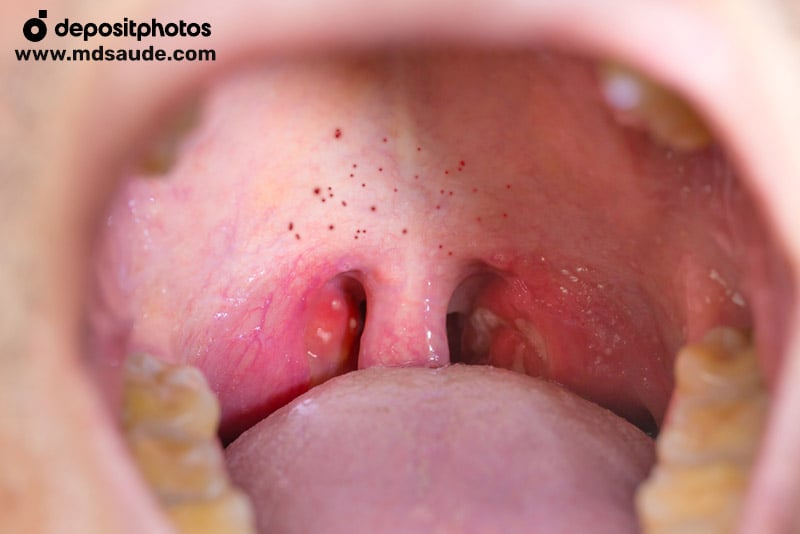
- Petechiae on the palate: in some cases, small red dots (petechiae) may appear on the palate, which is a common feature of streptococcal pharyngitis.
References
- Evaluation of sore throat in children – UpToDate.
- Evaluation of acute pharyngitis in adults – UpToDate.
- Acute Pharyngitis in Adults – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Images: personal archive, Wikimedia Commons, and Depositphotos.
Author(s)
Médico graduado pela Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), com títulos de especialista em Medicina Interna e Nefrologia pela Universidade Estadual do Rio de Janeiro (UERJ), Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia (SBN), Universidade do Porto e pelo Colégio de Especialidade de Nefrologia de Portugal.




![Pictures: Syphilis – All stages [Warning: Strong Images]](https://www.mdsaude.com/wp-content/uploads/sifilis-imagem.jpg)